New guidelines released for management of adult Covid patients. Read here
Ten News Network

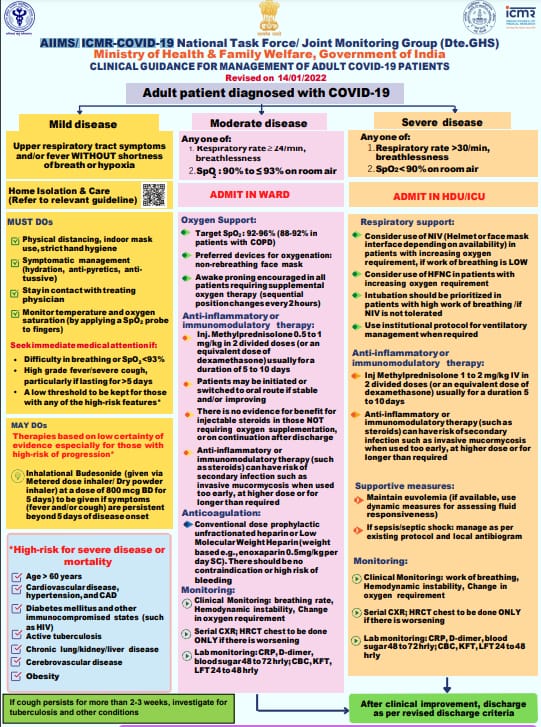
New Delhi, January 18: Amid the continual surge of COVID-19 cases across India, the COVID-19 National Task Force under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare on Monday released clinical guidance for the management of adult COVID-19 patients.
The guidelines released for the mild, moderate, severe cases states that, while mild cases will be home isolated, severe patients will be admitted in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) & moderate patients will have to be admitted in the ward.
The COVID-19 Task Force for mild cases has suggested home isolation with physical distancing, indoor mask use, and strict hand hygiene.
Patients with mild COVID-19 cases will experience fever without shortness of breath or hypoxia and upper respiratory tract.
Must-Dos for Mild cases:
•Symptomatic management (hydration, anti-pyretics, antitussive).
•Stay in contact with treating physician
•Monitor temperature and oxygen saturation (by applying a SpO2 probe to fingers)
Seek Immediate Attention if:
Difficulty in breathing or oxygen saturation drops below 93, or high grade fever/severe cough, particularly if lasting for more than 5 days.
Moderate cases will experience breathlessness and the SpO2 in the room temperature will be between 90 to 93%
Moderate cases are advised to be Admitted in the ward. Patients with such cases will be given Oxygen support:
•Target SpO2 : 92-96% (88-92% in patients with COPD)
• Preferred devices for oxygenation: non-rebreathing face mask
•Awake proning is encouraged in all patients requiring supplemental oxygen therapy (sequential position changes every 2 hours).
Severe COVID cases will experience major breathlessness and the SpO2 in the room temperature will be less than 90%. Such patients are advised to be admitted in HDU/ICU:
•The patient will be put on Respiratory support
•Use of NIV in patients with increasing oxygen requirements
•Intubation should be prioritised if the patient not responding to NIV
•Use of institutional ventilatory management when required
•Constant clinical monitoring will be required for breathing rate, Hemodynamic Instability